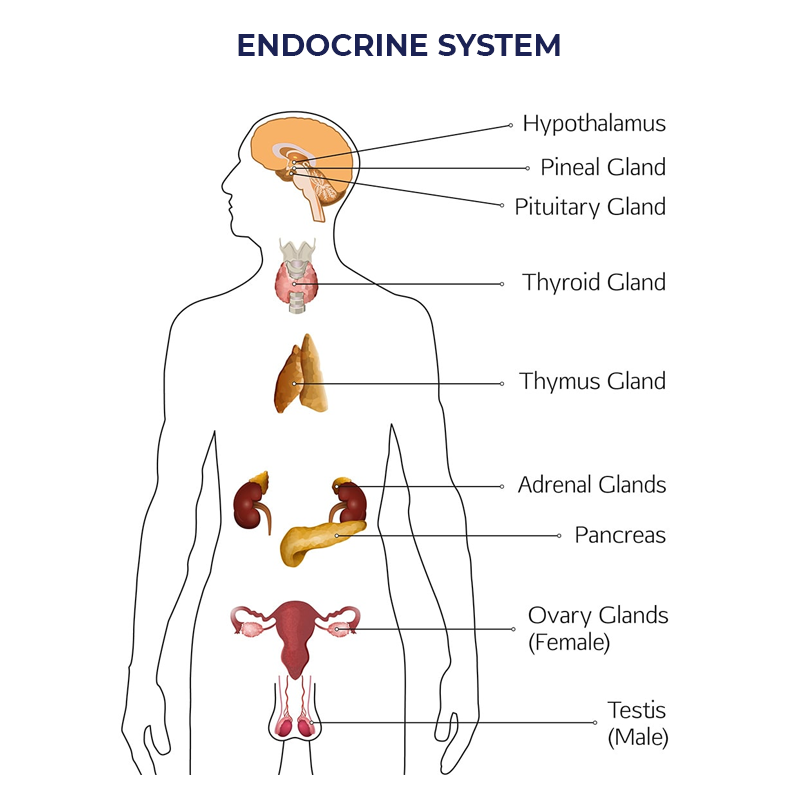
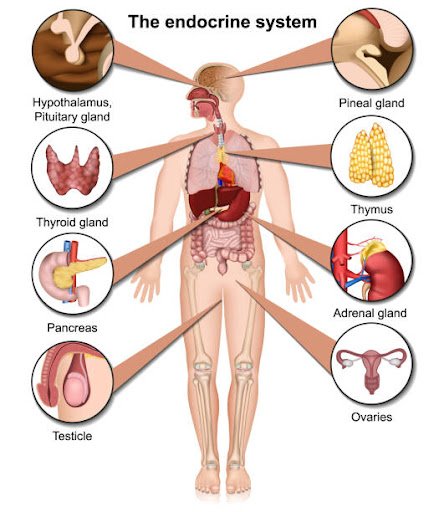
Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the “master gland,” the pituitary gland regulates the activity of other endocrine glands and controls functions such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
Thyroid Gland: This butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and overall growth and development.
Parathyroid Glands: These small glands, located behind the thyroid, play a critical role in regulating calcium levels in the body through the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH).
Adrenal Glands: Situated on top of each kidney, these glands produce hormones involved in stress response, metabolism, immune function, and blood pressure regulation.
Pancreas: The pancreas has both endocrine and exocrine functions. Its endocrine role involves the secretion of insulin and glucagon, hormones essential for regulating blood sugar levels.
Gonads: The ovaries in females and testes in males produce sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone) that are vital for reproductive functions and secondary sexual characteristics.